
Today automotive air conditioning is standard equipment on cars and trucks. Just 30 years ago this would’ve been considered a luxury option.
Since this is one of the more troublesome systems, often leading to very high repair bills, it seemed only right to cover it in depth. On this page we’ll start with the basic theory of operation.
At the bottom are links to advanced articles on individual components. You can find out what’s wrong with your car today by examining these common problem areas. Remember that It’s a lot easier to diagnose and repair AC systems with the basic knowledge of how they work.
Therefore, reading and learning about them isn’t a waste of time. Especially when you consider this area of the retail car repair business can be at times shady. When educated consumers start asking questions, estimates have a tendency to go down and automobiles fixed right on the first visit go up.
Auto Air Conditioning Design
All ac systems are designed to pump heat from one point to another. Commonly we remove heat from the inside and take it outside. The basic theory states, heat will flow from the warmer object to the colder one.
The greater the temperature difference between the two, the more heat flows. The substance used to remove the heat from the inside of an automobile is called refrigerant.
On older automotive air conditioning systems the factory installed refrigerant was R12. An amendment to the United States Clean Air Act has mandated that we phase out R12 as the refrigerant of choice.
Since air conditioning systems with R12 are susceptible to leaks, ozone damage and environmental concerns pushed for the replacement of this refrigerant.
This was finally adopted into United States law as a requirement in 1995. It started a new wave of AC specialty shops that performed conversions.
Car-makers began using R134-A as the freon of choice replacing r-12. In 2014 GM started using HFO-1234yf, believed to cause less damage to the ozone when released into the atmosphere.
Mercedes-Benz will start using a CO2 refrigerant called R744 in 2017 models. Auto AC service will be more complicated going forward as HFO and CO2 types aren’t compatible with the widely used R-freons.
Although the most common R 134 A air-conditioning systems operate in the same way with the same basic components as the R12 and HFO units keep in mind none of the refrigerants are interchangeable.
The HFO-1234yf goes a step further and runs at different pressures. All three use different lubrication oil for the compressor. Shops will have to get ready to service 4 different kinds of Freon.
And consumers will have to pay more for repairs as compliance becomes more difficult. If you are unsure of what type of Freon is in your vehicle, there are under hood labels identifying which type is installed.
Also the R12 service fittings are threaded connections and much smaller than their 134 counterparts that utilize a quick disconnect style service fitting. I have an article about converting old R12 to the new style freon below. Reading it can help avoid common problems.
Air Conditioning System Basic Operation

To understand how car ac refrigerant is used to cool the interior of the vehicle the effects of pressure and temperature should be understood first. If the pressure is high so is its temperature.
If the pressure of the refrigerant is low then again so is its temperature. High PSI lines are small diameter and hot. Low side lines are larger and cold to the touch.
Therefore, changing its pressure from a high pressure to a low pressure can easily change the temperature of the refrigerant. Temperature and pressure of the refrigerant is kept low inside the vehicle.
It’s circulated through a highly efficient heat ex-changer. This component is known as the evaporator. The component is pictured above on the right. It works in reverse of the engine coolant radiator. Heat from the passenger compartment is transferred to this device and passed to the Freon.
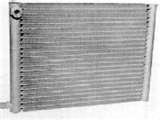
The heated refrigerant is then pumped forward to the air conditioning condenser, which is yet another heat exchange component.
It’s located in the front of the engine compartment. A condenser fan is used to blow fresh air across the coils and aluminum fins to remove the absorbed and stored heat within the refrigerant.
The evaporator on the inside of the vehicle and the condenser on the outside of the vehicle are solely responsible for the heat transfer properties of the entire system.
These two components are supported and operated by the other parts of the automotive air conditioning system. More in-depth description of these components will be available in the articles below.
Automobile Air Conditioning Help
Learning about A/C is important, because it can cost a lot or a little to repair. See a textbook example with this video about rip-off car ac repair.
Automotive AC can be one dangerous system to work on. Take a minute to review my page about automotive air conditioning safety.
The 5 car ac components that make the air blow cold. Learn how they work together to remove the heat from your automobile. Also see one of the best simplified diagrams for automotive air conditioning.
Now you know how the AC makes cold air it’s time to connect a set of manifold gauges and get some pressure readings. This is how to find out what is wrong with your car AC.
Dodge blower motor problems are becoming so common they’re offering the repair kits on E-bay. Learn more about the issues and an important step to take to prevent repeat failure.
If you own a General Motors car or truck built in the 2000s decade I’m thinking you will have HVAC issues at some point. Here’s four common problems with GM blower fans and climate control systems.
There is a lot of automobile air information on this page and I hope you do go through it all. But if you are in a hurry I have condensed some of the most important points and include some common car AC problems.
Freon leaking is one of the most common problems that will cause the ac to blow warm. Learn how to how to locate automotive ac leaks.
Now that the Freon leak is fixed its time to charge the system. This is a critical step in the cooling properly process. Learn the right way to recharge car ac. Often the first indication of an AC problem is a strange noise. Some sounds are completely normal while others need diagnosis. I wrote this article to help sort out the good from the bad air-conditioning noises. Electrical issues with car air conditioners can cause the same complaint of my air blows hot. Learn what to look for and see how a little corrosion can cause air conditioning electrical problems. Speaking of ac electrical problems one complaint that is common is interior fan noise or poor air flow. This next page gets you up to speed on diagnosing the blower motor. Now that the air is blowing what can we do when the air flow is weak or coming out of the wrong vents. This next page should help with your car ac airflow problems.
When it comes to replacing failed parts on your car a compressor is one of the most expensive. Learn the proper replacement procedure and how to protect your new car ac compressor. A lot of people have had problems with car air conditioners after conversion from R-12. Usually this has to do with improper conversion methods. If you want your cold air to last then learn the proper procedure for retrofitting auto ac systems. See why recovering and pulling a vacuum on the AC is so important for max cooling and reliability. Also see an interesting combo tool package for car ac charging.
Repeat complaints of the AC blows warm is a common problem. See some common causes of comebacks when it comes to auto AC repairs.
If you need one on one help with your automobile air conditioning problem you can visit the page for car repair help.
Find out what else is covered on this auto repair website and also more about the mechanic that built it on the home page. This next link takes you there from this page about automotive air conditioning.

